Safe and Sustainable Liquid Waste Disposal: Your Go-To Service Provider
Safe and Sustainable Liquid Waste Disposal: Your Go-To Service Provider
Blog Article
How Liquid Waste Disposal Works: A Comprehensive Introduction of Techniques and Technologies Used
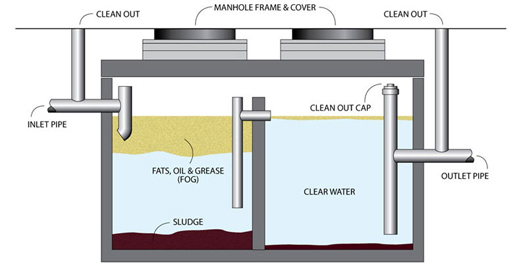
Review of Liquid Waste Kind
The complexity of liquid waste types requires a thorough understanding of their qualities and ramifications for disposal. Liquid waste can broadly be classified right into a number of kinds, including commercial, local, farming, and harmful waste. Each classification displays distinct properties, requiring details monitoring approaches to alleviate environmental and health threats.
Industrial fluid waste originates from manufacturing procedures and usually has a series of pollutants, such as heavy steels, solvents, and organic compounds. Municipal fluid waste, mostly comprising wastewater from households and business facilities, includes organic issue, nutrients, and virus (industrial wastewater treatment). Agricultural fluid waste, consisting of drainage from ranches, might have plant foods, pesticides, and animal waste, posturing dangers to water quality and communities
Unsafe fluid waste is characterized by its poisoning, sensitivity, or potential to create damage. This category consists of compounds like acids, bases, and certain chemicals that necessitate rigorous handling and disposal procedures. Comprehending these diverse fluid waste types is vital for establishing reliable disposal techniques and guaranteeing compliance with ecological policies. Proper category and characterization are necessary for applying ideal therapy methods and minimizing the adverse influences on public wellness and the atmosphere.
Physical Treatment Methods

Screening is the initial action, where larger particles and particles are eliminated from the liquid waste making use of displays or grates. In sedimentation tanks, heavier fragments work out at the bottom, creating a sludge layer, while the cleared up liquid can be more treated.
Filtration is an additional crucial technique that involves passing the fluid with porous products, such as sand or membranes, to record smaller fragments. This action enhances the top quality of the liquid, making it ideal for subsequent therapy procedures.

Chemical Treatment Methods
Chemical treatment methods are important for efficiently taking care of liquid waste, particularly in addressing liquified and colloidal contaminants that physical approaches may not properly get rid of. These methods utilize various chemical representatives to neutralize, speed up, or transform harmful substances right into less dangerous forms.
One typical method is coagulation and flocculation, where chemicals such as alum or ferric chloride are included to promote the gathering of suspended fragments. This process enhances sedimentation, enabling less complicated elimination of the resulting sludge. Additionally, oxidation procedures, employing representatives like chlorine or ozone, are utilized to damage down intricate organic compounds and pathogens, providing the waste more secure for discharge or further treatment.
Neutralization is one more important method, which readjusts the pH of acidic or alkaline explanation waste streams to neutral degrees, avoiding prospective injury to downstream systems and the setting. Furthermore, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) utilize combinations of oxidants and ultraviolet light to break down relentless toxins, attaining a higher level of treatment effectiveness.
Organic Therapy Procedures
Organic therapy procedures play a vital duty in the monitoring of fluid waste by making use of microbes to decompose raw check it out material and minimize pollutant degrees. These procedures can be broadly categorized into cardiovascular and anaerobic therapies, each using specific microbial communities to achieve effective waste degradation.
Cardiovascular treatment includes using oxygen to promote the breakdown of organic materials by germs. This procedure is typically applied in activated sludge systems, where oygenation storage tanks give a conducive setting for microbial development, resulting in the oxidation of natural contaminants. The resultant biomass can be divided from dealt with effluent via sedimentation.
On the other hand, anaerobic therapy takes place in the lack of oxygen, relying upon different bacteria to break down organic matter. This method is particularly beneficial for high-strength waste, as it creates biogas, a sustainable power resource, while decreasing sludge production. Technologies such as anaerobic digesters are often utilized in local and industrial applications.
Both aerobic and anaerobic organic treatments not just reduce the ecological effect of fluid waste but additionally help with source healing, making them important parts of sustainable waste management techniques. Their efficiency, flexibility, and efficiency sustain their widespread implementation throughout numerous industries.
Arising Technologies in Disposal
Cutting-edge methods to fluid garbage disposal are rapidly developing, driven by innovations in technology and a boosting focus on sustainability. Amongst these arising technologies, membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have actually obtained traction for their ability to integrate organic treatment with membrane filtering, leading to high-quality effluent that can be recycled in numerous applications. MBRs allow smaller footprints and a lot more efficient procedures contrasted to conventional systems.
One more encouraging advancement is using anaerobic digestion incorporated with nutrient recuperation modern technologies, which not just deals with fluid waste however likewise produces biogas and recuperates beneficial nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. This twin advantage improves resource effectiveness and decreases environmental More hints effect.
Furthermore, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) are being taken on for the degradation of complex natural toxins. These techniques use effective oxidants and drivers to break down contaminants at the molecular level, offering a highly efficient solution for challenging waste streams.
Moreover, the assimilation of fabricated knowledge and device learning in waste monitoring systems is enhancing operational performance and anticipating maintenance, bring about minimized prices and enhanced environmental conformity. These innovations mirror a considerable shift in the direction of more lasting and efficient liquid garbage disposal methods.
Conclusion
In verdict, effective fluid waste disposal demands a thorough understanding of different techniques and modern technologies. The assimilation of physical, chemical, and biological treatment techniques ensures the reliable administration of diverse waste kinds. Moreover, the development of innovative technologies enhances treatment efficiency and promotes sustainability in waste management techniques. By continually progressing these techniques, it comes to be feasible to attend to the growing challenges associated with fluid waste, eventually contributing to ecological protection and resource healing.
Fluid waste disposal is an essential aspect of ecological monitoring, requiring an extensive understanding of different strategies and modern technologies tailored to different waste kinds. Liquid waste can broadly be classified right into several kinds, including commercial, municipal, agricultural, and hazardous waste. Agricultural liquid waste, consisting of runoff from ranches, might include fertilizers, pesticides, and pet waste, presenting threats to water top quality and ecosystems.
Different physical therapy methods play a critical duty in managing liquid waste effectively - industrial wastewater treatment.In conclusion, reliable fluid waste disposal requires a detailed understanding of different techniques and technologies
Report this page